std::condition_variable
条件变量std::condition_variable有wait和notify接口用于线程间的同步。如下图所示,Thread 2阻塞在wait接口,Thread 1通过notify接口通知Thread 2继续执行。
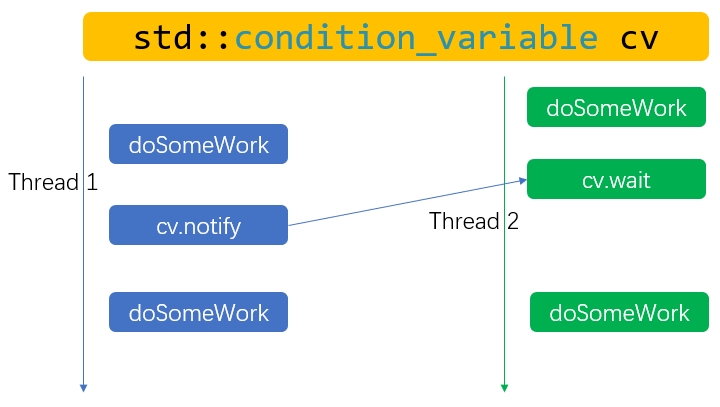
具体参见示例代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
std::mutex mt;
std::queue data;
std::condition_variable cv;
auto start=std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
void logCurrentTime()
{
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto elapsed = std::chrono::duration_cast<:chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count();
std::cout lk(mt);
//wait first for notification
cv.wait(lk); //it must accept a unique_lock parameter to wait
while (!data.empty())
{
logCurrentTime();
std::cout 输出结果
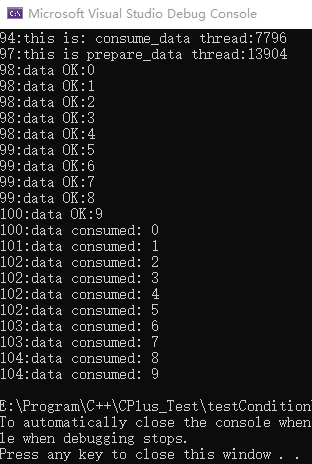
分析
主线程中另启两个线程,分别执行consume_data和prepare_data,其中consume_data要先执行,以保证先等待再通知,否则若先通知再等待就死锁了。首先consume_data线程在从wait 处阻塞等待。后prepare_data线程中依次向队列写入0-10,写完之后通过notify_one 通知consume_data线程解除阻塞,依次读取0-10。
std::future
std::future与std::async配合异步执行代码,再通过wait或get接口阻塞当前线程等待结果。如下图所示,Thread 2中future接口的get或wait接口会阻塞当前线程,std::async异步开启的新线程Thread1执行结束后,将结果存于std::future后通知Thread 1获取结果后继续执行.
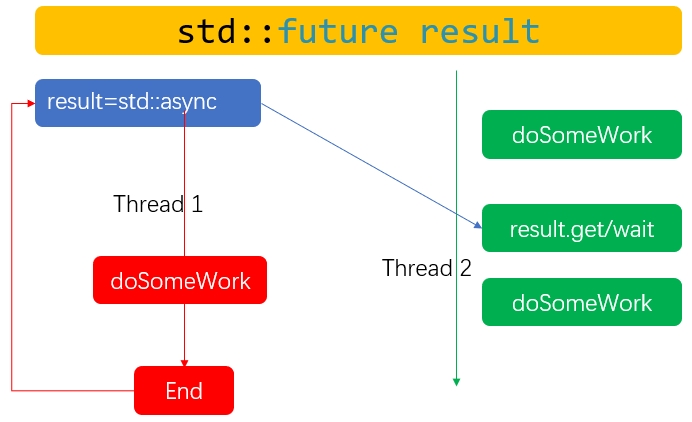
具体参见如下代码:
#include
#include
#include
int test()
{
std::cout result = std::async(test);
std::cout 输出结果
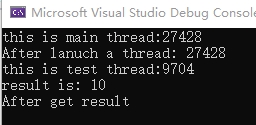
分析
主程序中调用std::async异步调用test函数,可以看到main函数的线程ID 27428与test函数执行的线程ID 9704并不一样,说明std::async另起了一个新的线程。在test线程中,先sleep 1000ms,所以可以看到”After lanuch a thread:”先输出,说明主线程异步执行,不受子线程影响。而”After get result “最后输出,说明get()方法会阻塞主线程,直到获取结果。
1.本站内容仅供参考,不作为任何法律依据。用户在使用本站内容时,应自行判断其真实性、准确性和完整性,并承担相应风险。
2.本站部分内容来源于互联网,仅用于交流学习研究知识,若侵犯了您的合法权益,请及时邮件或站内私信与本站联系,我们将尽快予以处理。
3.本文采用知识共享 署名4.0国际许可协议 [BY-NC-SA] 进行授权
4.根据《计算机软件保护条例》第十七条规定“为了学习和研究软件内含的设计思想和原理,通过安装、显示、传输或者存储软件等方式使用软件的,可以不经软件著作权人许可,不向其支付报酬。”您需知晓本站所有内容资源均来源于网络,仅供用户交流学习与研究使用,版权归属原版权方所有,版权争议与本站无关,用户本人下载后不能用作商业或非法用途,需在24个小时之内从您的电脑中彻底删除上述内容,否则后果均由用户承担责任;如果您访问和下载此文件,表示您同意只将此文件用于参考、学习而非其他用途,否则一切后果请您自行承担,如果您喜欢该程序,请支持正版软件,购买注册,得到更好的正版服务。
5.本站是非经营性个人站点,所有软件信息均来自网络,所有资源仅供学习参考研究目的,并不贩卖软件,不存在任何商业目的及用途





暂无评论内容